Home Campus Bookshelves Howard University General Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach Unit 1: Atomic Structure
Atomic Structure: Atoms and Atomic Orbitals | SparkNotes
Nov 9, 2023Describe the atomic orbital shown in this picture. A) 2pz B) 2py C) 2px D) 3px E) 3py cookiemonster020 is waiting for your help. Add your answer and earn points. plus Add answer +7 pts Expert-Verified Answer No one rated this answer yet — why not be the first? 😎 pstnonsonjoku
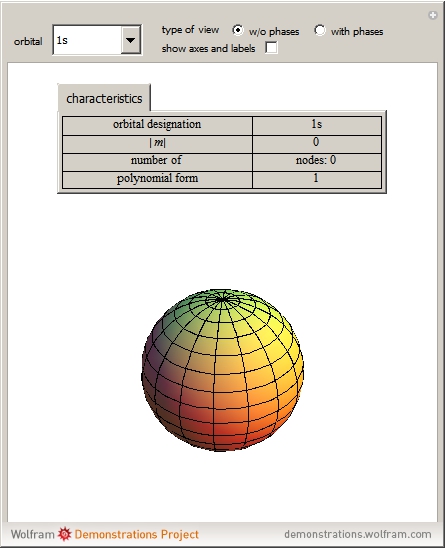
Source Image: demonstrations.wolfram.com
Download Image
The quantum numbers n = 1 and ℓ = 0 describe a small spherical wave with no nodes, the quantum numbers n = 2 and ℓ = 0 describe a larger spherical wave with a single node, and the quantum numbers n = 3 and ℓ = 0 describe an even larger spherical wave with two nodes. These waves all look slightly different, as shown in Figure 6.16.

Source Image: byjus.com
Download Image
Build Your Own Atom Model: Fun & Easy Science for Kids | Kids Activities Blog Now in the model that you have drawn, you have shown the electron as a particle which means you are sticking with Bohr’s model of an atom and therefore, it does not make much sense to talk about ‘orbitals’ per se. Now, where do orbitals come in? Orbitals come in when you accept an electron’s dual nature.

Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Describe The Atomic Orbital Shown In This Picture
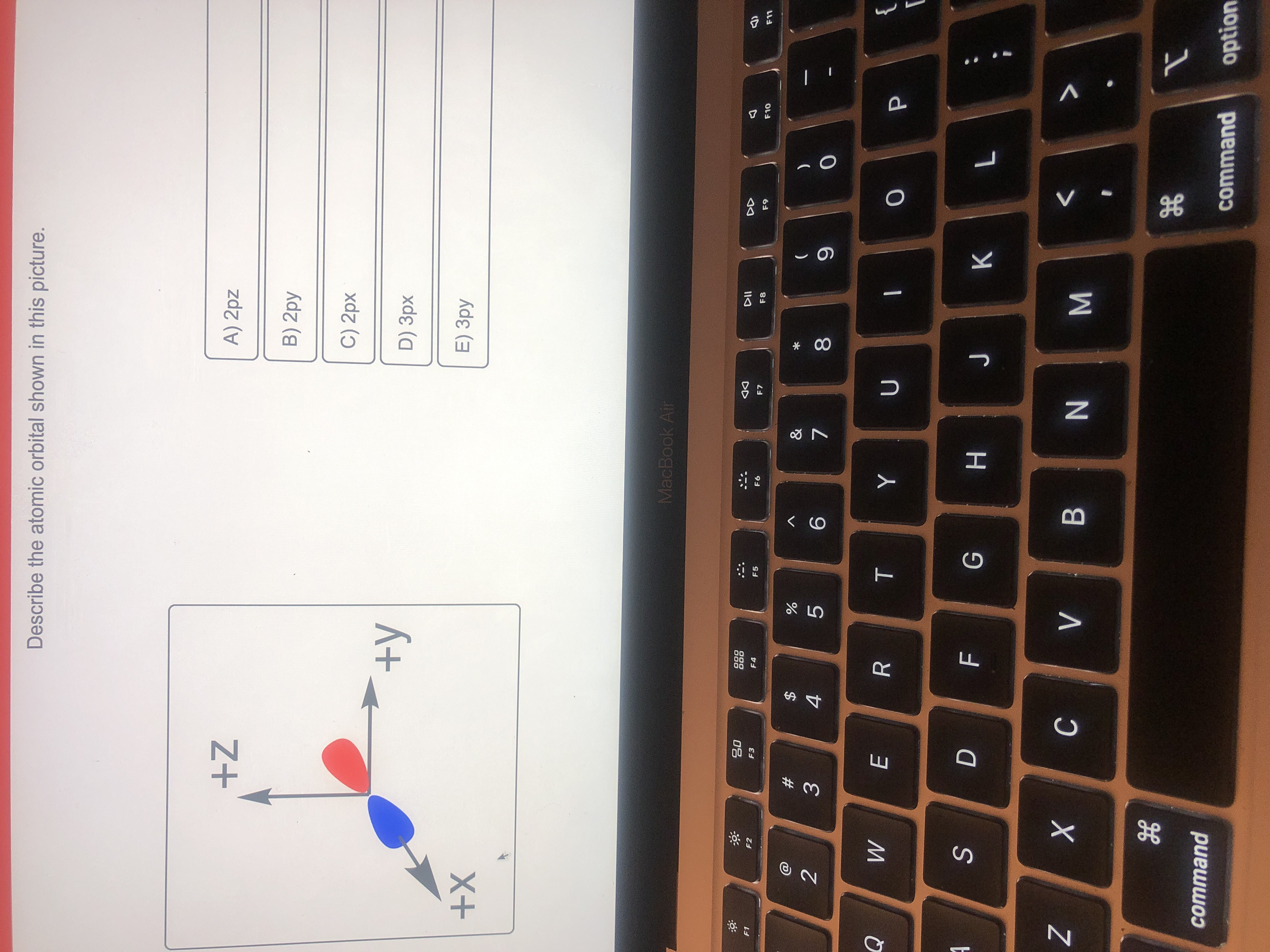
Now in the model that you have drawn, you have shown the electron as a particle which means you are sticking with Bohr’s model of an atom and therefore, it does not make much sense to talk about ‘orbitals’ per se. Now, where do orbitals come in? Orbitals come in when you accept an electron’s dual nature. Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers Question 46 of 1 Describe the atomic orbital shown in this picture. +Z A) 2pz B) 3pz C) 4pz D) 2px +y E) 3px +X This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer
Solved Describe the atomic orbital shown in this picture. | Chegg.com
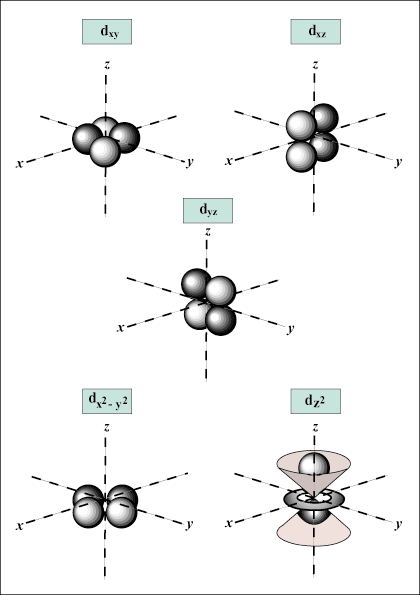
Atomic orbitals are the basic building blocks of the atomic orbital model (or electron cloud or wave mechanics model), a modern framework for visualizing the submicroscopic behavior of electrons in matter. Atomic Orbital Vs. Molecular Orbital – Online Organic Chemistry Tutor
Source Image: onlineorganicchemistrytutor.com
Download Image
Shapes of Atomic Orbitals: Shape Determination – SPD, Videos, Examples Atomic orbitals are the basic building blocks of the atomic orbital model (or electron cloud or wave mechanics model), a modern framework for visualizing the submicroscopic behavior of electrons in matter.

Source Image: toppr.com
Download Image
Atomic Structure: Atoms and Atomic Orbitals | SparkNotes Home Campus Bookshelves Howard University General Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach Unit 1: Atomic Structure
Source Image: sparknotes.com
Download Image
Build Your Own Atom Model: Fun & Easy Science for Kids | Kids Activities Blog The quantum numbers n = 1 and ℓ = 0 describe a small spherical wave with no nodes, the quantum numbers n = 2 and ℓ = 0 describe a larger spherical wave with a single node, and the quantum numbers n = 3 and ℓ = 0 describe an even larger spherical wave with two nodes. These waves all look slightly different, as shown in Figure 6.16.

Source Image: kidsactivitiesblog.com
Download Image
Molecular Orbital Theory | Concept & Diagrams – Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com Show how radial density changes as the radius increases. Atomic Orbitals Atomic orbitals are (energy) states or wave forms of electrons in the atom. If we insist on the particle nature of electrons, then the probability of finding an electron in an atomic orbital is proportional to the square of the wavefunction.

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
Answered: Describe the atomic orbital shown in… | bartleby Now in the model that you have drawn, you have shown the electron as a particle which means you are sticking with Bohr’s model of an atom and therefore, it does not make much sense to talk about ‘orbitals’ per se. Now, where do orbitals come in? Orbitals come in when you accept an electron’s dual nature.
Source Image: bartleby.com
Download Image
Physics Reference: Physics 9702 Doubts | Help Page 205 Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers Question 46 of 1 Describe the atomic orbital shown in this picture. +Z A) 2pz B) 3pz C) 4pz D) 2px +y E) 3px +X This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer

Source Image: physics-ref.blogspot.com
Download Image
Shapes of Atomic Orbitals: Shape Determination – SPD, Videos, Examples
Physics Reference: Physics 9702 Doubts | Help Page 205 Nov 9, 2023Describe the atomic orbital shown in this picture. A) 2pz B) 2py C) 2px D) 3px E) 3py cookiemonster020 is waiting for your help. Add your answer and earn points. plus Add answer +7 pts Expert-Verified Answer No one rated this answer yet — why not be the first? 😎 pstnonsonjoku
Build Your Own Atom Model: Fun & Easy Science for Kids | Kids Activities Blog Answered: Describe the atomic orbital shown in… | bartleby Show how radial density changes as the radius increases. Atomic Orbitals Atomic orbitals are (energy) states or wave forms of electrons in the atom. If we insist on the particle nature of electrons, then the probability of finding an electron in an atomic orbital is proportional to the square of the wavefunction.